Peroneal tendinopathy
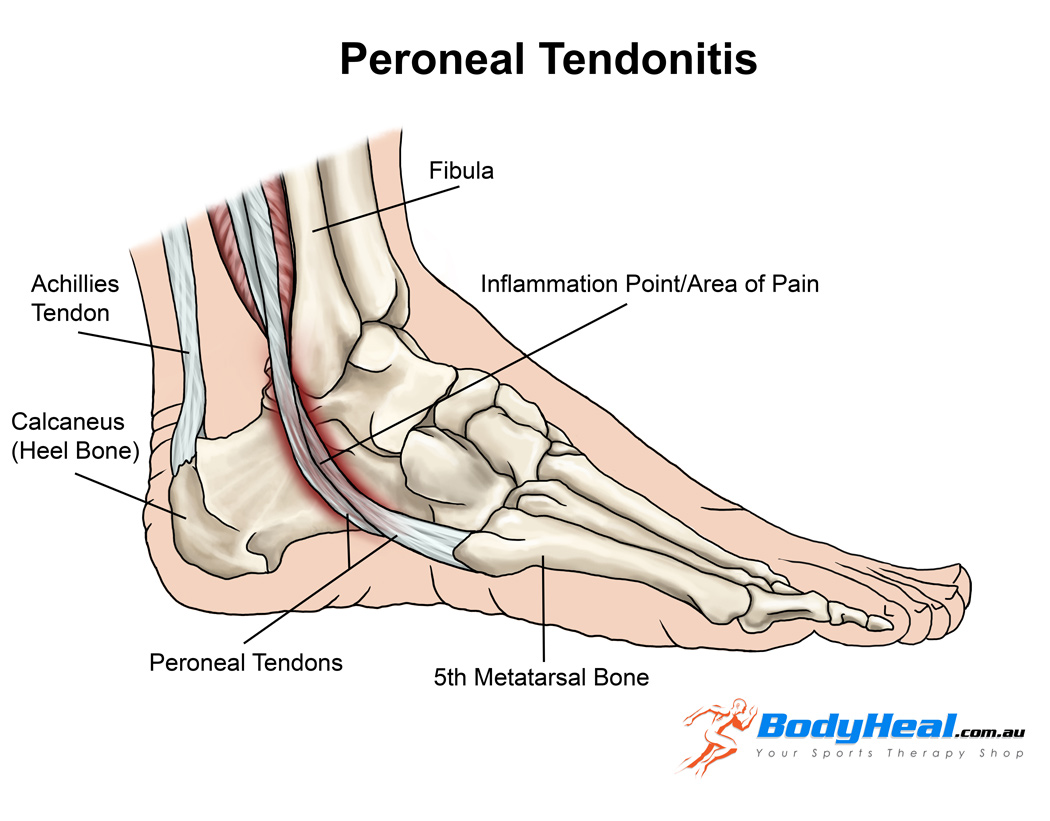
Peroneal tendinopathy or peroneal tendonitis is characterized by an aching pain and swelling in the perineal tendons. These are located in the lower, outside portion of the ankle. A tendon is soft-tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone. The muscles involved in this condition are the 2 peroneal muscles in the lower leg, called the peroneus longus and the peroneus brevis.
Anatomy
?There are two peroneal tendons that run along the back of the fibula. The first is called the peroneus brevis. The term “brevis” implies short. It is called this because it has a shorter muscle and starts lower in the leg. It then runs down around the back of the bone called the fibula on the outside of the leg and connects to the side of the foot. The peroneus longus takes its name because it has a longer course. It starts higher on the leg and runs all the way underneath the foot to connect on the other side of the foot. Both tendons, however, share the major job of turning the ankle to the outside. The tendons are held in a groove behind the back of the fibula bone.
Causes of Peroneal Tendonitis
- A sudden increase in weight bearing activities, particularly walking, running or jumping
- Inadequate or unsupportive footwear
- Muscle imbalances of the lower limb
Poor lower limb biomechanics - Incomplete rehabilitation following an acute ankle injury, such as an ankle sprain
Symptoms of Peroneal Tendinopathy
- Gradual worsening pain over the outside of the ankle
- Pain during and/or after weight bearing activities
Pain with turning the foot in and/or out - Instability around the ankle when weight bearing
Diagnosis
A full examination from a physiotherapist can be all thats needed to diagnose peroneal tendonitis
Patients with this condition usually experience pain behind the outside ankle during activities putting stress on the perineal tendons. Pain can also be noticed following these activities or following a rest period. This may be noticed especially upon waking in the morning. There may be swelling when the injury first happens. There will also be pain when testing resisted foot movements. Stretches into various positions of the foot inversion, and resisted movements can cause pain behind the outside ankle.
Diagnosis may be confirmed with an MRI scan or ultrasound investigation
a diagnostic Ultrasound may be used for detecting all types of peroneal injuries.
What else could it be?:
Symptoms of peroneal tendinopathy mimic various other conditions of the ankle joint. So, before diagnosing peroneal tendinopathy we should rule out other possible injuries by doing the following tests:
Ankle Sprain: ligament testing by the Physiotherapist
Ankle fractures: special tests by the Physiotherapist
Os trigonum syndrome: MRI, physiotherapy testing
Chronical lateral ankle pain with other cause: MRI
Longitudinal peroneal tendon tear: MRI
Peroneal subluxation: ultrasonography, CT, MRI or peroneal tenography
Flexor Hallucis longus tendon injury
Physiotherapy rehabilitation
Treatment for peroneal tendonitis includes a program of stretching, strengthening, mobilisation and manipulation. It also includes proprioceptive exercises, icing, ankle bracing or k-taping during contact sports. If symptoms are severe, a cast or ROM boot immobilization may be worn for 10-20 days. After symptoms resolve, you will begin a progressive rehabilitation programme along with a gradual increase to full activity.
The use of a biomechanical ankle platform (BAPS), deep tissue friction massage, ultrasound electric stimulation can also be included in the physiotherapy
Also, shock wave therapy (ESWT), acupuncture is used to treat tendinopathy. But there is only limited evidence from studies for these treatments.
There is evidence for using manual therapy, specifically the lateral calcaneal glide.
If you have any further queries please call PhysioNow. Our experienced physiotherapists would be happy to help you. Call Today to get started 289-724-0448.!