How do Headaches occur?
There are many different types of headaches with many different causes. Many people may blame it on the weather, stress, or work, and feel like it is out of their control and that nothing can help their headaches. If this sounds like you, there is treatment available and you do not have to live with your pain. Headaches that stem from your neck or jaw are treatable through physiotherapy and can result in a decreased intensity and frequency or even stop them completely. However, migraines can also be manageable with rehab.
What are headaches from the neck?
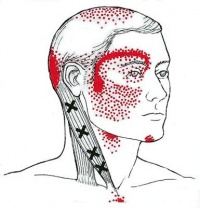
Headaches that stem from the neck are known as cervicogenic headaches and are a type of referred pain. Referred pain means that the pain actually originates from another part of the body, and not the place where you actually feel the pain. Moreover, the head pain is actually coming from problems in the tissues and/or joints in the neck.
Common symptoms of cervicogenic headaches include:
- Firstly, one-sided headaches
- Second, neck stiffness
- Decreased motion in the neck
- Radiating pain to the eyes, shoulder, or arms
- Lastly, they are triggered by certain neck positions or movements
What are headaches from the jaw?
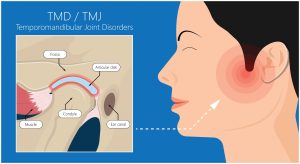 Headaches stemming from the jaw result from dysfunction in the jaw joint, anatomically known as the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). This joint connects your lower jaw to the skull and is used in actions such as talking and chewing as it allows the opening and closing of the mouth. Therefore, headaches are one of the common symptoms of jaw dysfunction. Though they are lesser known, it is commonly missed as a source.
Headaches stemming from the jaw result from dysfunction in the jaw joint, anatomically known as the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). This joint connects your lower jaw to the skull and is used in actions such as talking and chewing as it allows the opening and closing of the mouth. Therefore, headaches are one of the common symptoms of jaw dysfunction. Though they are lesser known, it is commonly missed as a source.
Common symptoms of TMJ dysfunction include:
- Clicking on the jaw
- Pain or tenderness with jaw movements (biting, talking, chewing, etc)
- Headaches, especially in the morning (due to grinding and clenching of the jaw during the night)
- Also, neck stiffness
How can physiotherapy help?
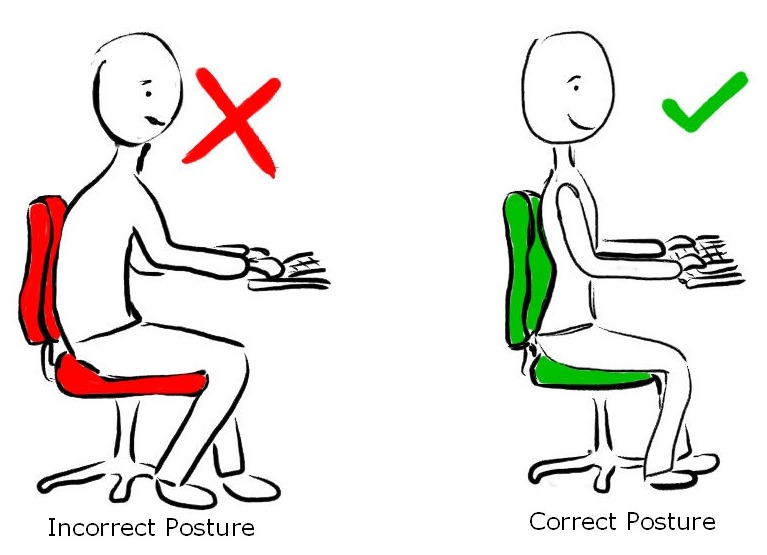
Your physiotherapist will provide a comprehensive assessment of your neck and jaw to determine a specific treatment plan for you. The evaluation may include observing your resting posture, and the way your jaw and neck move. Also, how much movement is available in your jaw and neck, and more.
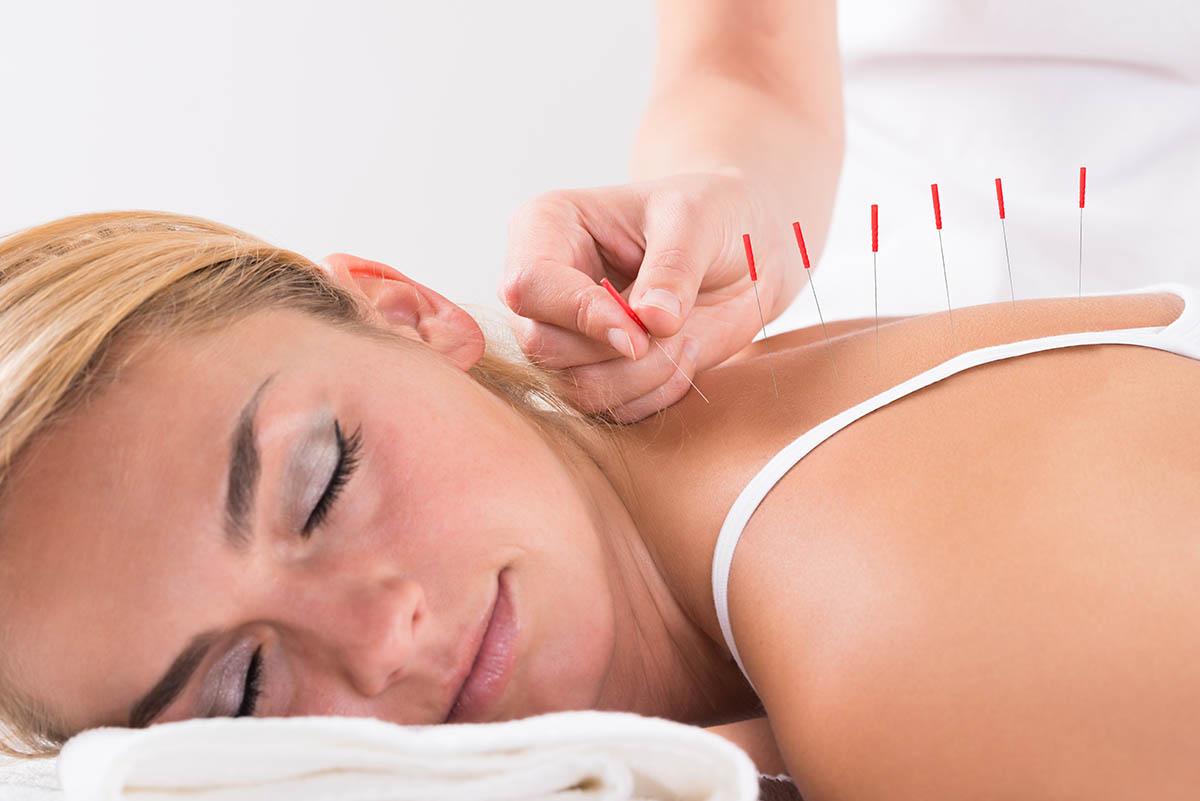
Your treatment plan may include strengthening weak muscles, correcting posture and faulty movement patterns, stretching and mobility exercises, manual therapy techniques like soft tissue massage and joint mobilizations to reduce pain and increase range of motion. They may use modalities like heat, electrotherapy and acupuncture as well depending on your condition and goals of treatment. Your physiotherapist will work closely with you to develop an individualized plan of treatment including a home exercise program, and education on self-management of your condition at home. They can also inform you and help you get in contact with other healthcare practitioners that may need to be involved in your care.
If you are experiencing persistent headaches, book with PhysioNow today for your first assessment and treatment!