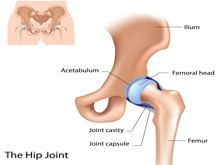
A hip fracture is a break in the upper quarter of the femur (thigh) bone. The extent of the break depends on the forces that are involved. The type of surgery used to treat a hip fracture is based on the bones and soft tissues affected or on the level of the fracture.
Older people are at a higher risk of hip fracture because bones tend to weaken with age (osteoporosis). Multiple medications, poor vision and balance problems also make older people more likely to trip and fall — one of the most common causes of hip fracture.
? Signs and symptoms of a hip fracture include:
• Inability to move immediately after a fall
• Severe pain in your hip or groin
• Inability to put weight on your leg on the side of your injured hip
• Stiffness, bruising and swelling in and around your hip area
• Shorter leg on the side of your injured hip
• Turning outward of your leg on the side of your injured hip
? Causes of Hip fracture
• falling on a hard surface or from a great height.
• blunt trauma to the hip, such as from a car crash.
• diseases such as osteoporosis, which is a condition that causes a loss of bone tissue.
• obesity, which leads to too much pressure on the hip bones.
? Types of Fractures
In general, there are three different types of hip fractures. The type of fracture depends on what area of the upper femur is involved.
Intracapsular Fracture
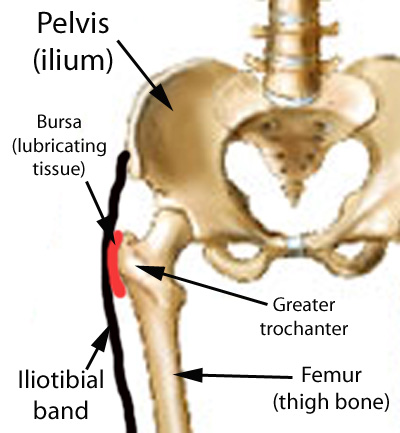
These fractures occur at the level of the neck and the head of the femur, and are generally within the capsule. The capsule is the soft-tissue envelope that contains the lubricating and nourishing fluid of the hip joint itself.
Intertrochanteric Fracture
This fracture occurs between the neck of the femur and a lower bony prominence called the lesser trochanter. The lesser trochanter is an attachment point for one of the major muscles of the hip. Intertrochanteric fractures generally cross in the area between the lesser trochanter and the greater trochanter. The greater trochanter is the bump you can feel under the skin on the outside of the hip. It acts as another muscle attachment point.
Subtrochanteric Fracture
This fracture occurs below the lesser trochanter, in a region that is between the lesser trochanter and an area approximately 2 1/2 inches below .
In more complicated cases, the amount of breakage of the bone can involve more than one of these zones. This is taken into consideration when surgical repair is considered.
Treatment for hip fracture: usually involves a combination of surgery, rehabilitation and medication.
? Surgery
The type of surgery you have generally depends on the location and severity of the fracture. Are the broken bones properly aligned? (displaced fracture. What is your age? What are your underlying health conditions?
The options include:
• Internal repair using screws. Metal screws are inserted into the bone to hold it together while the fracture heals. Sometimes screws are attached to a metal plate that runs down the upper thigh.
• Partial hip replacement. If the ends of the broken bone are not lined up or damaged, your surgeon may remove the head and neck of the femur and install a metal replacement (prosthesis).
• Total hip replacement. Your upper thigh and your hip socket are replaced with an artificial one (prostheses). Total hip replacement may be a good option if arthritis or a prior injury has damaged your joint. This may have been affecting your hip function even before the fracture.
? Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is begun as soon as possible after hip fracture surgery, often within a day. The initial goals are to help people retain the level of strength they had before the fracture. You want to keep moving to prevent loss of muscle. You also want to prevent problems that result from bed rest. The ultimate goal is to restore your ability to walk properly without a limp.
Benefits of Rehab
Rehab will help you:
• Restore normal movement in your joint
• Build up strength in the joint and surrounding muscles
• Ease pain and swelling
• Let you get back to your normal activities including walking without a limp
• Help with circulation, particularly right after surgery, so you don’t have problems with blood clots
If you have or someone you know has fractured a hip or had hip replacement surgery, please call PhysioNow. Our experienced physiotherapists would be happy to help with your recovery! Call today to book an appointment!