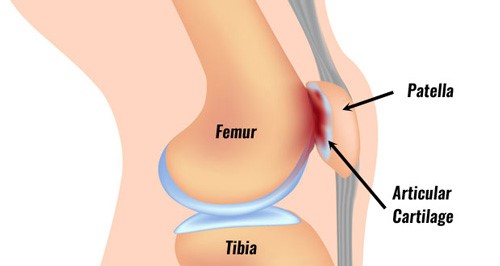
Patellofemoral pain syndrome happens when your knee cap does not track properly. The knee joint consist of two joints. The tibiofemoral joint which is between the two long bones in your leg and the second one is the patellofemoral joint. This is between the femoral condyle (end of thigh bone) and the knee cap. The cartilage on the back of the knee cap glides on the cartilage on the front of the condyles of the femur. The knee cap usually sits in a snug groove at the end of the thigh bone.
Knee movements are controlled by a number of muscles connected to the knee cap. Your thigh muscle helps to stabilize the knee cap and enables it to move smoothly in the groove. When this is pulled out of the groove, you can develop Patellofemoral pain syndrome.
Causes of Patellofemoral pain syndrome or Anterior knee pain
Patellofemoral pain syndrome, is one of the most common causes of pain in the knee. Pain is usually felt under the knee cap. This is where it glides on the femur/thigh bone. If you have patellofemoral pain syndrome, it hurts when you bend and straighten your knee . There are a number of factors which can cause the pain.
Common Causes of Patellofemoral pain syndrome
- Weakness in the hip and thigh muscles-Weakness in the thigh muscles can cause increased load which may lead to pain. Pain in your knees will further limit the activity of your muscles and over time can cause further weakness. Weakness of the inner thigh muscle will affect the movement of the knee cap as you do your normal activities. Weakness in your hip muscles also can affect activities like climbing stairs and walking.
- Excessive loading or rapid increase in the load for muscles around the knee-Depending on your usual activities, your knee will have a level of activity that is tolerated by your joint. Rapid increases in loading of activity may lead to a highly irritable or sensitive joint. This can cause Patellofemoral pain syndrome.
- Posture or position of hip, knee and feet-Flat feet or excessive turning in of feet can change movement mechanics further up the leg and cause excessive strain in your knee cap.
- Tight muscles around the knee-Tightness in the muscles can reduce the movement of your knee and affect how your joint works . This will lead to excessive loading during activities. The common muscles that become tight are your hamstrings, Quadriceps, Iliotibial band and calf.
- Previous injury or dislocation of knee cap
- Desk top work, where a lot of sitting can cause pressure on the kneecap.
- Irritation of fat pad around the knee
- Tendinitis of quadriceps tendon
- Bursitis around the knee
- Osteoarthritis
When poor biomechanics are repeated with each step of your walking and running it may lead to a highly sensitive joint and Patellofemoral pain syndrome.
Symptoms
- The onset of knee cap pain is normally gradual rather than traumatic.
- Pain at the front, back and sides of the knee with or without swelling.
- Bending and straightening of knee can cause pain.
- Pain after prolonged sitting or when you keep the knee bent for longer periods of time.
- Clicking or grinding when you bend or straighten your knee.
- Pain when you go up and down the stairs, up hill /down hill, squatting, running or jumping.
- Poor knee control or stiffness
Physiotherapy Treatment
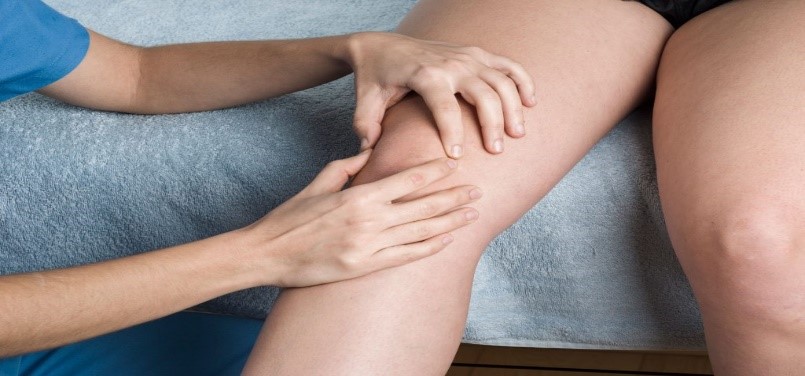
- Physiotherapy is the most effective treatment for short- and long-term management of Patellofemoral pain syndrome. Your Physiotherapist will fully assess you on your first visit to identify your functional limitation. They will also help to set goals and identify contributing factors for the pain. They will provide a customized rehabilitation program.
- In the initial phase of rehabilitation, treatment is directed towards reducing the pain, swelling and muscle inhibition. To do this PhysioNow will use electrotherapy modalities, acupuncture, rest, taping, gentle motion or joint mobilization and muscle setting exercises.
- Once the pain and swelling reduces, treatment is focused towards modifying the factors that have been identified as a cause for the problem.
- Rehabilitation typically emphasizes increasing strength and pain free movements. It also will address postural correction, improving the stability of the pelvis, balance and functional abilities.
- Stretching exercises to address the tight muscles and strengthening the weak muscles will improve your load tolerance.
- Successful rehabilitation requires adherence to your exercise program .
- You will also need to reduce the aggravating movements and slowly build the endurance and strength for those activities over time.
- Prior to discharge you will be given a safe progression of exercises and functional activities.
- For long term management, your foot and knee control will be assessed by your Physiotherapist.
- As a result, you may require custom foot orthotics to correct your foot position.
- This will help to improve foot and knee control.
- Others might need a hip stabilization program and your Physiotherapist will be happy to discuss with you the long term rehabilitation plans if this is needed.
How long it will take to get better?
We expect to see improvements with Physiotherapy over a 3 to 6-month period. Further improvements continue beyond this period. Adherence to your specific exercise program is important in maintaining the improvement. Most people will get back to their normal function with rehabilitation in the short term. Many patients can continue in their chosen activity during rehabilitation. Some modification of activity may be all that is needed.
If you play sports, you will need to do sports specific exercises to ensure a safe return to sports. It is good to wear proper supporting footwear to help keep your feet in a good position. This will improve alignment of your knees.
How to book an appointment with a Physiotherapist at PhysioNow?
We have four Physiotherapy clinics of which three are located in Mississauga and one is in Etobicoke. You can call 289-724-0448 to book into any of these clinics for an appointment with a Physiotherapist.
Most of the time we can arrange your initial visit on the same day in a location which is nearest to you. Your initial appointment will be a one to one 40-60 minute session with a Physiotherapist which includes treatment as well on the first day.
Your follow up appointments will typically take 40 minutes. Normally, we would recommend 2 to 3 sessions per week depending on the factors identified on initial assessment, treatment plan and your goals. If you have limited funding available, we will be happy to work with you to develop a home exercise program.
Please call today to get started on your treatment for Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome at PhysioNow!