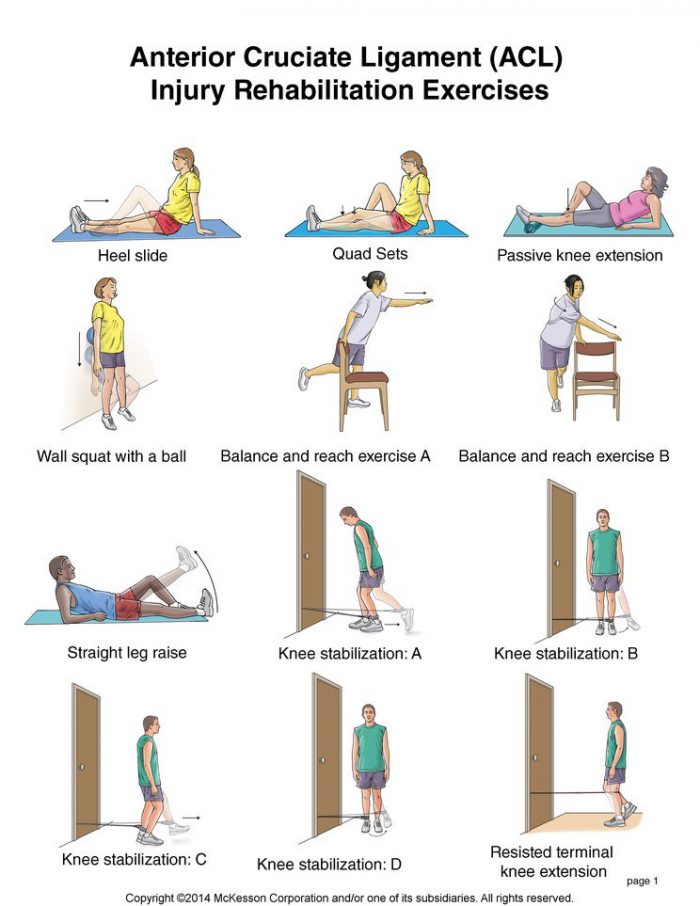
ACL injuries are very common. Most people know at least one other person who has gone through some kind of ACL injury. But what exactly is the ACL? Furthermore, what is ACL Rehabilitation?
ACL Rehabilitation is a term used to describe the physiotherapy treatment that takes place after an ACL injury. It is an important part of the recovery so that individuals can get back to their work and sport
ACL Rehabilitation – What is the relevant Anatomy
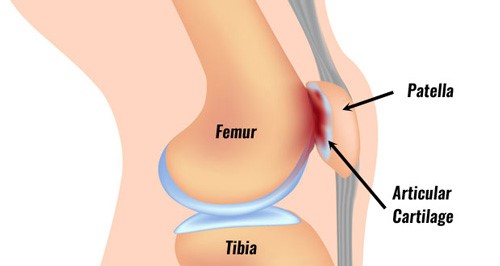
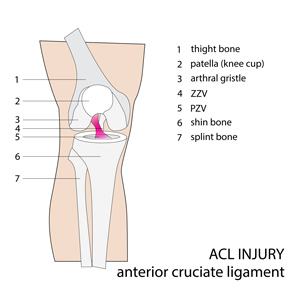
The term ACL stands for Anterior Cruciate Ligament. Ligaments are soft tissues that connect 2 bones together. Ligaments provide stability to the joint. The ACL is found in the knee joint. It is one of the most important ligaments in the knee.
ACL Rehabilitation – Where is the ACL located?
The ACL is one of two ligaments found deep inside the knee joint. The other ligament is called the PCL, or Posterior Cruciate Ligament. These ligaments cross each other inside the joint, forming an “X”. Together, they help keep the thigh bone (femur) connected to the shin bone (tibia). The ACL stops the shin bone from sliding out in front of the thigh bone. The PCL stops the shin bone from sliding back on the thigh bone.
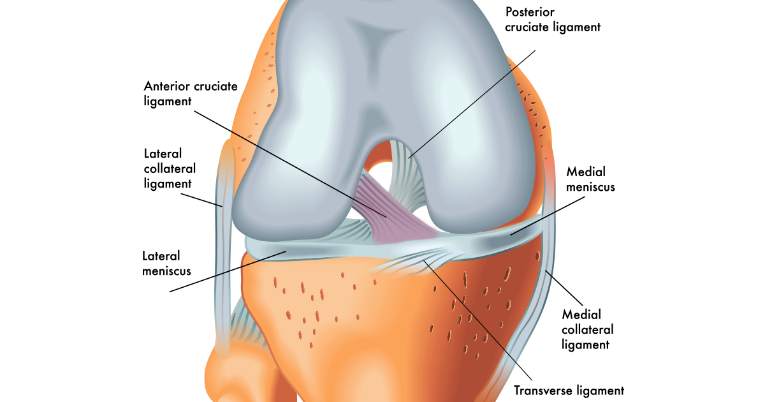
ACL anatomy
ACL Rehabilitation – What is the function of the ACL?
The ACL is more commonly injured than the PCL. This is likely because the PCL is wider and stronger than the ACL. However, the ACL is more important to the overall function of the knee. Injury to the ACL means that there is too much forward movement of the shin bone. This has huge impacts on the stability of the knee, especially when doing any weight-bearing activities.
What are some of the signs and symptoms of an ACL injury?
- A loud ‘pop’ or a ‘popping’ sensation in the knee
- Severe knee pain and unable to put weight through the knee
- Immediate swelling of the knee
- Loss of range of motion
- A feeling of instability or ‘giving way’ with weight bearing
How does the ACL get injured?
Another important part of ACL Rehabilitation is understanding how the injury happened. This information helps explain why the injury happened and may help prevent a re-injury. Specifically, the ACL can be injured in many ways. Some examples of mechanisms of injury include:
- Quickly changing direction while running
- Suddenly slowing down or stopping
- Incorrectly landing from a jump
- Twisting the knee with the foot planted on the ground
- Direct blow to the knee
What are some of the risk factors for ACL injury?
For ACL Rehabilitation to be successful, there has to be an understanding of risk factors.
- Firstly, female gender seems to be a risk factor
- Women have a higher incidence of ACL injuries according to the research
- There are a variety of factors, including differences in anatomy, muscle strength and hormones
- Additionally, certain sports have more risk for ACL injury
- Sports that involve a lot of sudden direction changes and collisions are more likely to result in ACL injuries
- Examples include soccer, football, basketball and downhill skiing
- Lastly, poor strength through the hips and lower legs is an overall risk for ACL injury
ACL injuries – Are they all the same?
ACL injuries can vary from person to person depending on the extent of the injury. The term for an injury to a ligament is called a sprain. Sprains are graded based on how severely the ligament is damaged.
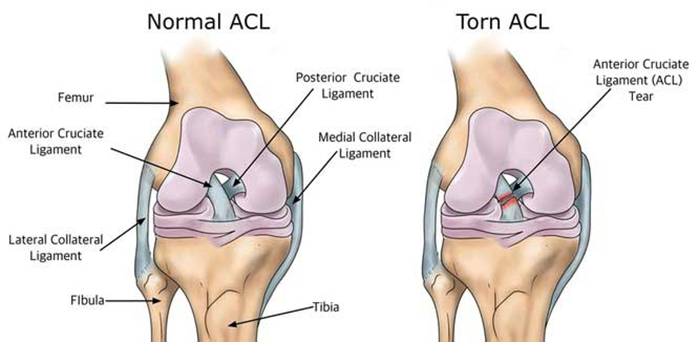
ACL Tear
Grade 1 – there is mild damage to the ligament
-
-
- The ligament is slightly stretched
- The knee joint is still stable
- There is no requirement for surgery.
-
Grade 2 – there is a partial tear in the ligament
-
-
- The ligament is stretched to the point where it becomes loose.
- There is still some stability in the knee joint.
- There is usually no requirement for surgery
-
Grade 3 – there is a complete tear or rupture in the ligament
-
-
- The ligament has been split into two pieces
- The knee joint is unstable
- Due to the level of damage, there is usually requirement for surgery
-
Additionally, other structures may be injured at the same time as the ACL. Specifically, a lot of patients who injure their ACL, also injure their Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) and/or medial meniscus. This combination increases the overall severity of the injury.
Unfortunately, ACL injuries can also lead to the early development of osteoarthritis in the knee. The arthritis can vary in severity depending on the person but can contribute to long term pain for some people.
How do we diagnose ACL injuries?
A doctor or Registered Physiotherapist can assess the knee after the injury. They may perform some physical tests that may confirm an ACL injury. However, these tests are not always 100% accurate. Additionally, with a very acute injury, it is difficult to complete the tests properly due to intense pain and swelling.
As a result, imaging is usually required to confirm an ACL injury. Understanding the severity of the injury is important because it will determine if surgery will be required.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging or MRI is the most commonly used imaging test to diagnose an ACL tear. An MRI uses radio waves and a strong magnetic field to create images of the tissues in the body. An MRI will be able to show the extent of an ACL injury and any other tissues that may have been damaged. However, there is usually a lot of swelling soon after the injury happens. As a result, an MRI is usually not done immediately afterwards.
ACL Rehabilitation – What are the treatment options?
Physiotherapy
-
- For grade 1 or 2 sprains, the treatment is usually conservative.
- This means that the doctor would refer the patient to physiotherapy to regain range of motion and strength.
- The physiotherapist will assess the patient and work on restoring their function
- The physiotherapy treatment may involve:
- Electrical modalities to reduce inflammation
- Hands on treatment to release muscle tension, promote circulation and improve flexibility
- Exercises to help regain range of motion and recover strength and function through the knee
- The physiotherapist may also recommend a custom knee brace to help protect the knee from instability
- Education regarding home management and using any necessary gait aids or braces if required
- The time required for recovery varies from patient to patient, but generally ranges from 8-12 weeks
Surgical repair
-
- For sprains that are severe, the family doctor will refer the patient to an orthopedic surgeon.
- The surgeon will assess the patient and determine if they need surgery for their injury
- Circumstances where surgery may be recommended include:
- The patient is an athlete and their sport involves a lot of jumping, cutting or pivoting movements
- There is injury to more than one structure in the knee
- The knee buckles regularly with everyday activities
How does surgery affect ACL Rehabilitation?
-
-
-
- Once the surgery is finished, there will be a recovery process
- Firstly, to keep the knee from bending, the patient will be placed in a brace
- Additionally, to be able to move around safely, the patient will be given crutches
- The surgeon will refer the patient for ACL Rehabilitation
- The surgery repairs the torn ligament, but the knee will not be able function normally at first
- Physiotherapy is needed to recover the knee movement, strength and stability.
-
-
-
- The recovery time after the surgery can range anywhere between 6-9 months. This can be up to 12 months if the patient is returning to high impact sports.
- For more information about ACL surgeries, please click here.
-
-
- However, there are some patients who can choose not to have the surgery if they can regain function through physiotherapy and if their lifestyle doesn’t place too much stress on the ACL.
- For example, surgery may not be needed for people who are:
-
- Relatively inactive
- Engage in moderate exercise and/or recreational activities
- Play sports that put less stress on the knees
-
Whichever treatment pathway the patient requires for their ACL injury, physiotherapists play a huge role in their recovery. It is important to seek out treatment as soon as possible to prevent chronic problems from developing. Furthermore, starting your treatment sooner than later, helps you get back to your life.
Call PhysioNow today to book your appointment!